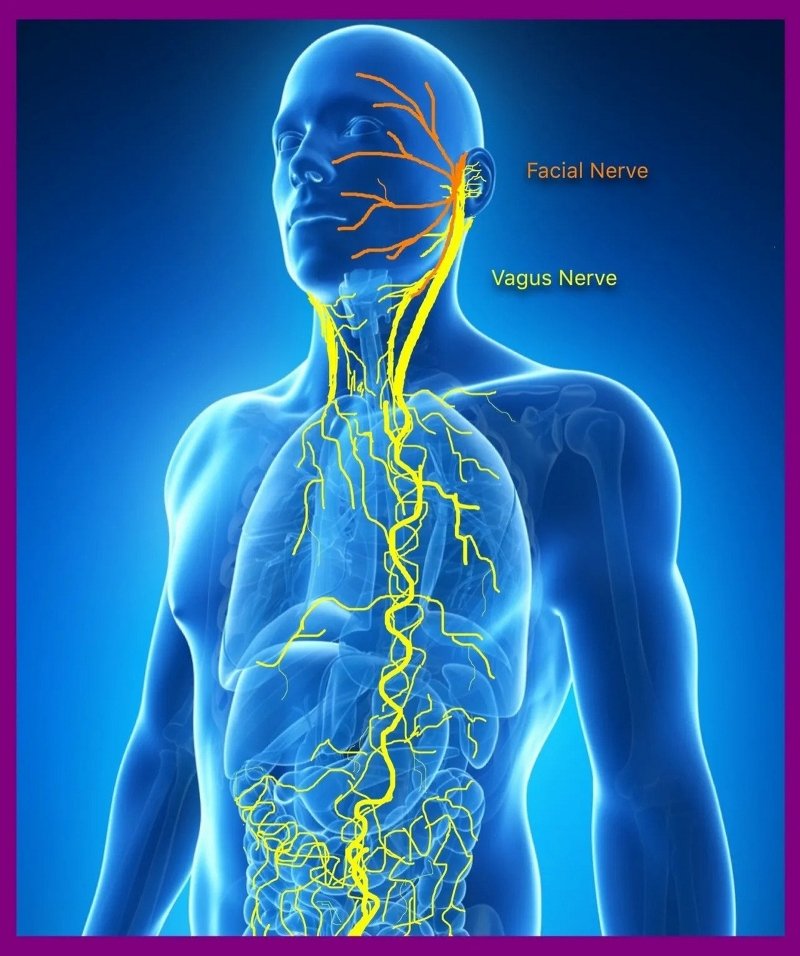
The Vagus Nerve
The Vagus nerve is sometimes called the wandering nerve because it is one of the longest and most complex nerves in the bod.
The Vagus nerve originates in the brainstem and travels down through the neck and chest to the abdomen.
The Vagus nerve is involved in turning on the parasympathetic nervous system, otherwise known as the body's "rest and digest" response. It controls numerous functions essential for our survival.
Some of the main functions of the Vagus Nerve include:
1. The Vagus nerve regulates breathing, heart rate, digestion, and metabolism. As well as controlling how the body detects and responds to stress, it also releases hormones that regulate emotions and mood. In addition, the Vagus nerve regulates the immune system and is linked to depression and anxiety.
2. The Vagus nerve regulates breathing by controlling the muscles involved in respiration. Also, it monitors blood oxygen and carbon dioxide levels.
3. Vagus nerves regulate the digestive process from the moment we smell, see, or taste food. As well as stimulating the release of digestive enzymes and juices, it also aids in moving food through the digestive system.
4. By reducing inflammation in the body, the vagus nerve modulates inflammation and regulates the immune system.
5. Blood glucose levels can be detected by the vagus nerve and insulin and glucose metabolism can be regulated by it.
6. Sensory information is sent to the brain from the organs in the thorax and abdomen, including the heart, lungs, liver, and digestive system.
7. Depression and anxiety can be treated by stimulating the vagus nerve, which has been shown to regulate mood and behavior.
Ultimately, the Vagus nerve is a crucial component of the autonomic nervous system, and its functions maintain homeostasis and promote health.
More on how the vagus nerve can affect digestion
Many of the digestive processes in the body are controlled by the vagus nerve and it plays a critical role in the digestive system.
1. Activating the Vagus nerve stimulates the release of digestive enzymes and increases blood flow to the digestive organs, including the stomach, liver, and pancreas. As a result, digestion and nutrient absorption are improved.
2. The Vagus nerve also regulates how food moves through the digestive system. Food is moved through the digestive tract by controlling the contractions and relaxations of the muscles in the stomach and intestines.
3. The Vagus nerve regulates stomach acid production, which is essential for breaking down food and killing harmful bacteria.
The Vagus nerve plays an important role in the digestive system, regulating many of the processes involved in digestion and ensuring that nutrients are absorbed properly from our food.
The Vagus nerve is responsible for creating the rest and digest state, which is necessary for proper digestion. Stress (fight or flight state) negatively impacts our gut health for this reason.
A key component of the parasympathetic nervous system, the vagus nerve calms the body and reduces stress.
The Vagus nerve can be stimulated in several ways, including:
1. Slow, deep breaths can stimulate the vagus nerve and activate the parasympathetic nervous system. Breathing techniques such as diaphragmatic breathing or box breathing can be used to achieve this.
2. Meditation stimulates the Vagus nerve and promotes relaxation. Meditation techniques that activate the parasympathetic nervous system include mindful breathing, body scans, and visualization.
3. Regular physical exercise stimulates the Vagus nerve and activates the parasympathetic nervous system. Jogging, cycling, and swimming are particularly effective aerobic exercises.
4. Exposure to cold water or air stimulates the Vagus nerve and activates the parasympathetic nervous system. Cryotherapy, cold showers, and ice baths can all be used to accomplish this.
5. Acupressure or massage of the neck and face can stimulate the Vagus nerve and activate the parasympathetic nervous system.
6. Singing or humming: Vocalization techniques such as singing or humming can also stimulate the Vagus nerve and activate the parasympathetic nervous system.